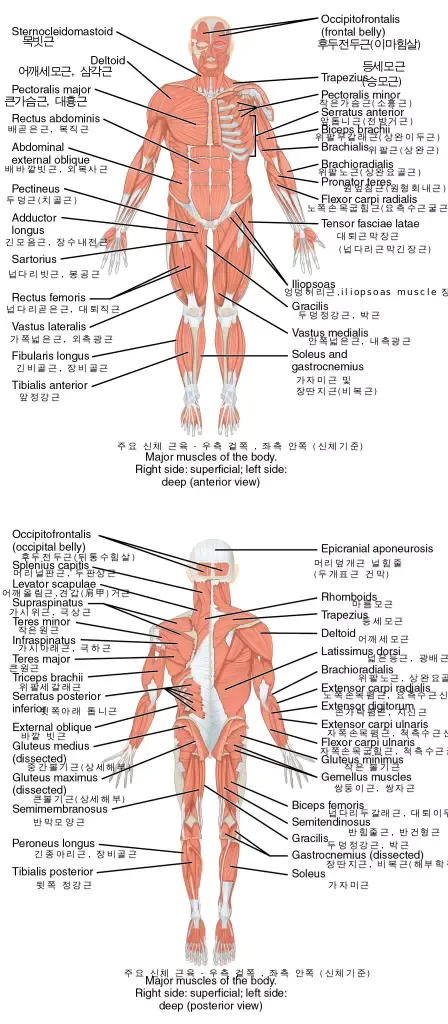
The human muscular system plays a crucial role in the body's overall functioning. Comprised of various muscle types, it works in tandem with the skeletal system to facilitate movement and support various internal functions. In this article, we will explore the muscular system's structure, anatomy, and function, as well as the different types of muscles and their respective roles in the body.
Understanding the Muscular System
The Role of the Muscular System
The primary function of the muscular system is to provide motor function, enabling the body to perform daily activities through muscle contractions. It is important to note that the muscular system does not operate in isolation but rather collaborates with other systems in the body, such as the skeletal system. This interconnectedness results in integrated motor function, allowing for seamless movement and support.
Muscular System Components
The muscular system comprises three main types of muscles:
- Skeletal muscles
- Smooth muscles
- Cardiac muscles
Each muscle type serves a unique purpose and function within the body. Let's delve deeper into the structure and role of these muscles.
Skeletal Muscles: The Framework for Movement
Skeletal muscles, also known as striated muscles due to their striped appearance under a microscope, are responsible for voluntary movement. These muscles attach to bones by tendons, forming the musculoskeletal system. There are over 600 skeletal muscles in the human body, accounting for approximately 40% of an individual's body weight.
Skeletal Muscle Anatomy
Skeletal muscles comprise muscle fibers, which can vary in size, shape, and arrangement. These fibers are enveloped by a connective tissue called the epimysium, while bundles of muscle fibers are encased in another connective tissue known as the perimysium. These connective tissues not only support and protect the muscles during contraction but also facilitate the passage of blood and nerves to each muscle.
Smooth Muscles: Regulating Internal Functions
Smooth muscles, found predominantly in the body's internal structures like the digestive tract and blood vessels, are involuntary muscles that control various internal functions. For example, smooth muscles in the respiratory tract and cardiovascular system regulate the diameter of bronchioles and blood flow, respectively.
Smooth Muscle Anatomy
Smooth muscles are non-striated, fusiform-shaped muscles, which are more elastic than their striated counterparts. This elasticity allows them to maintain contractile tone for extended periods, as evidenced in the urinary bladder.
Cardiac Muscles: The Heart's Powerhouse
Cardiac muscles are specialized, involuntary muscles found exclusively in the heart. Responsible for the heartbeat, these muscles contract rhythmically, ensuring the continuous circulation of blood throughout the body.
Cardiac Muscle Anatomy
Cardiac muscle cells are rectangular in shape, with a single central nucleus and a rich supply of mitochondria and myoglobin to produce and store energy. They are surrounded by a barrier called the sarcolemma, which separates the intracellular and extracellular content.
Muscular System Disorders
Various disorders can affect the muscular system, impacting either the muscles themselves or the nerves and neurotransmitters surrounding them. Examples of such disorders include multiple sclerosis, myopathy, muscular dystrophy, and peripheral neuropathy.
Maintaining and Strengthening the Muscular System
Maintaining and strengthening the muscular system is crucial for overall health, as it not only enhances physical performance but also prevents injuries and age-related muscular decline. Here, we will discuss various strategies and practices that can help maintain and improve the health of the muscular system.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular exercise is essential for maintaining the health and strength of the muscular system. Incorporating a variety of exercises, such as aerobic activities, resistance training, and flexibility exercises, can help target different muscle groups and promote overall muscular health.
- Aerobic exercises, such as running, swimming, and cycling, can help increase cardiovascular endurance and improve the efficiency of the cardiac muscles.
- Resistance training, which includes weight lifting and bodyweight exercises, can help build and maintain muscle mass, improve bone density, and boost metabolic rate.
- Flexibility exercises, such as yoga and stretching, can help improve muscle elasticity and joint mobility, reducing the risk of injuries and improving overall movement quality.
Nutrition
A balanced and nutrient-rich diet is crucial for supporting the health of the muscular system. Consuming adequate protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats can provide the necessary building blocks for muscle repair, growth, and function.
- Protein: Essential for muscle repair and growth, protein can be found in various sources, including lean meats, fish, poultry, eggs, dairy products, legumes, and nuts.
- Carbohydrates: The primary source of energy for muscles, carbohydrates can be found in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes.
- Healthy fats: Necessary for hormone production and joint health, healthy fats can be obtained from sources such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil.
Rest and Recovery
Adequate rest and recovery are vital for the health and function of the muscular system. Muscles need time to repair and grow after exercise, and insufficient rest can lead to fatigue, injury, and decreased performance. Ensuring proper sleep, incorporating rest days, and using recovery techniques like foam rolling and massage can help promote muscular health and performance.
Preventing Injuries
Taking precautions to prevent injuries is critical for maintaining the health of the muscular system. Practicing proper form during exercise, warming up before physical activity, and gradually increasing the intensity and duration of workouts can help minimize the risk of injuries. Additionally, seeking guidance from fitness professionals or physical therapists can provide valuable insights into injury prevention and safe exercise practices.
The Importance of Muscular Health
In conclusion, the muscular system plays a vital role in the body's overall functioning and well-being. By prioritizing exercise, nutrition, rest, and injury prevention, individuals can maintain and enhance the health of their muscular system, promoting a strong, resilient, and functional body.
Common Muscular System Disorders and Treatment
Muscular system disorders can affect the function, strength, and mobility of muscles. Understanding these disorders and their treatments can help individuals manage symptoms and maintain a better quality of life. Here, we will discuss some common muscular system disorders and their respective treatments.
Muscular Dystrophy
Muscular dystrophy is a group of genetic disorders that cause progressive muscle weakness and loss of muscle mass. While there is no cure for muscular dystrophy, treatment can help manage symptoms and slow disease progression. Treatment options include:
- Physical therapy: To maintain mobility, flexibility, and muscle strength.
- Occupational therapy: To develop adaptive strategies and improve the quality of daily living.
- Medication: Corticosteroids may be prescribed to slow muscle deterioration.
- Assistive devices: Braces, wheelchairs, and other devices can help maintain mobility and independence.
Myopathy
Myopathies are a group of muscle diseases characterized by muscle weakness, inflammation, or degeneration. Treatment depends on the specific type of myopathy and may include:
- Medication: Anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants, and other medications can help manage symptoms and slow disease progression.
- Physical therapy: To maintain muscle strength, flexibility, and function.
- Lifestyle changes: Maintaining a healthy weight, regular exercise, and a balanced diet can help improve overall health and well-being.
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
Multiple sclerosis is an autoimmune disorder that affects the central nervous system, causing muscle weakness, spasms, and stiffness. While there is no cure for MS, treatment can help manage symptoms and slow disease progression. Treatment options include:
- Medication: Disease-modifying drugs, muscle relaxants, and other medications can help manage symptoms and slow disease progression.
- Physical therapy: To maintain muscle strength, flexibility, and function.
- Occupational therapy: To develop adaptive strategies and improve the quality of daily living.
Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy refers to damage or dysfunction of the peripheral nerves, leading to muscle weakness, numbness, and pain. Treatment for peripheral neuropathy depends on the underlying cause and may include:
- Medication: Pain relievers, anti-seizure medications, and antidepressants can help manage symptoms.
- Physical therapy: To maintain muscle strength, flexibility, and function.
- Lifestyle changes: Managing underlying conditions like diabetes, maintaining a healthy weight, and incorporating regular exercise can help improve overall health and well-being.
Maintaining Muscular Health in the Presence of Disorders
Living with a muscular system disorder can be challenging, but by working closely with healthcare professionals, individuals can develop personalized treatment plans to manage symptoms and maintain their quality of life. Emphasizing a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate rest can help support overall health and well-being, even in the presence of muscular system disorders.
Muscle Cramps and Prevention
Muscle cramps are involuntary, sudden contractions of one or more muscles. They can be painful and often occur in the legs, especially the calf muscles. Although muscle cramps are usually harmless, they can be uncomfortable and disruptive. Some common causes of muscle cramps include dehydration, muscle overuse, and electrolyte imbalances. To prevent muscle cramps, consider the following strategies:
- Stay hydrated: Drink enough water throughout the day, especially during exercise or hot weather.
- Stretch regularly: Incorporate stretching exercises into your daily routine to maintain flexibility and prevent muscle tightness.
- Proper nutrition: Ensure a balanced diet rich in nutrients like potassium, calcium, and magnesium, which play a vital role in muscle function.
- Warm-up before exercise: Prepare your muscles for physical activity with a gentle warm-up, like light aerobic exercise or dynamic stretching.
- Gradually increase exercise intensity: Avoid sudden increases in physical activity, and allow your muscles to adapt to new challenges gradually.
Muscle Fatigue and Recovery
Muscle fatigue is a normal response to physical exertion and occurs when muscles can no longer generate enough force to maintain their level of activity. Prolonged or intense exercise can lead to muscle fatigue, which may result in decreased performance, soreness, and a reduced range of motion. To promote muscle recovery and prevent excessive fatigue, consider the following strategies:
- Adequate rest: Ensure sufficient rest between workout sessions to allow your muscles to repair and recover.
- Sleep: Prioritize quality sleep, as it plays a critical role in muscle recovery and overall well-being.
- Nutrition: Consume a balanced diet rich in protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats to support muscle repair and growth.
- Active recovery: Engage in light, low-impact activities like walking, swimming, or yoga on rest days to maintain blood flow and promote muscle recovery.
- Massage and foam rolling: Utilize massage techniques or foam rolling to alleviate muscle tightness, improve flexibility, and promote circulation.
By incorporating these strategies into your daily routine, you can support your muscular system's overall health and well-being, minimize the risk of injuries, and enhance your physical performance.
Conclusion
The human muscular system is a complex and vital component of the body's overall functioning. Comprising skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles, it facilitates movement, supports internal processes, and powers the heart. Understanding the structure, anatomy, and function of the muscular system can offer valuable insights into the body's capabilities and potential for growth and healing.