The nervous system is one of the most complex and vital systems in the human body. It is responsible for the communication between different parts of the body, and it controls all our voluntary and involuntary functions. The nervous system is made up of nerve cells called neurons that transmit messages throughout the body.
The Structure of the Nervous System
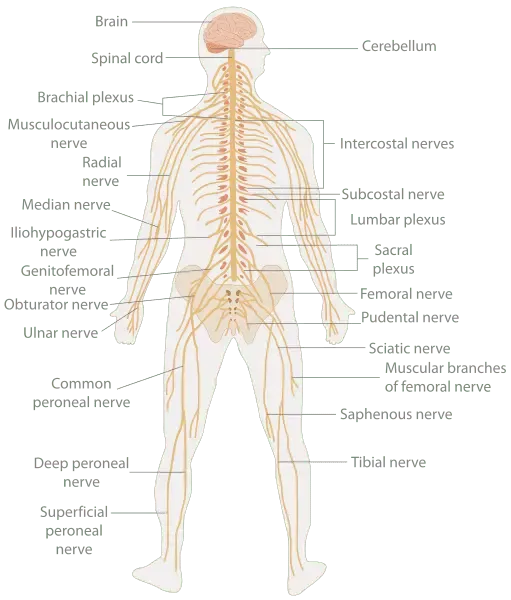
The nervous system is divided into two main parts: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS)./p>
The Central Nervous System (CNS)
The CNS includes the nerves in the brain and spinal cord, and is safely contained within the skull and vertebral canal of the spine.
The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
All of the other nerves in the body are part of the PNS. The PNS is further divided into two parts: the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system.
The Somatic Nervous System
The somatic nervous system controls all the things that we are aware of and can consciously influence, such as moving our arms, legs and other parts of the body.
The Autonomic Nervous System
The autonomic nervous system regulates the processes in the body that we cannot consciously influence. It is constantly active, regulating things such as breathing, heart beat, and metabolic processes.
The autonomic nervous system is further divided into three parts:
- The sympathetic nervous system. This system prepares your body for physical and mental activity. It makes your heart beat faster and stronger, opens your airways so you can breathe more easily, and inhibits digestion.
- The parasympathetic nervous system. This system is responsible for bodily functions when we are at rest: it stimulates digestion, activates various metabolic processes, and helps us to relax.
- The enteric (gastrointestinal) nervous system. It is a separate nervous system for the bowel, which, to a great extent, autonomously regulates bowel motility in digestion.
The sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems usually do opposite things in the body. But these two systems do not always work in opposite directions; they sometimes complement each other too.
The Nervous System and Sensory Input
The nervous system receives information through our senses, which include sight, hearing, taste, smell, and touch. When we receive sensory input, it is transmitted to the CNS via neurons. The CNS then processes this information and sends out appropriate responses.
For example, when we touch a hot plate, sensory neurons in the skin send a signal to the spinal cord, which in turn sends a signal to the brain. The brain then processes this information and sends out a signal to the muscles, causing them to contract and pull the hand away from the hot plate.
The Nervous System and Motor Output
The nervous system also controls our voluntary and involuntary movements. Voluntary movements are those that we consciously control, such as moving our arms or legs. Involuntary movements are those that occur without our conscious control, such as the beating of our heart or the contraction of our digestive muscles.
Voluntary movements are controlled by the somatic nervous system, which is part of the PNS. This system consists of neurons that transmit information from the CNS to the muscles.
Involuntary movements, on the other hand, are controlled by the autonomic nervous system (ANS), which is also part of the PNS. The ANS regulates our body's internal environment, such as breathing, heart rate, and digestion.
The ANS is divided into two branches: the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. The sympathetic nervous system prepares the body for action by increasing heart rate, dilating airways, and inhibiting digestion. The parasympathetic nervous system, on the other hand, conserves energy and promotes relaxation by stimulating digestion and slowing heart rate.
The Nervous System and Neurons
Neurons are the building blocks of the nervous system. They are specialized cells that transmit information in the form of electrical and chemical signals. Neurons have three main parts: the cell body, dendrites, and axons.
Dendrites are the short branches that receive signals from other neurons and transmit them to the cell body. Axons are the long branches that transmit signals away from the cell body to other neurons or muscles.
- Cell body: also known as the soma, contains the nucleus and other organelles necessary for the neuron's survival and function.
- Dendrites: branch-like structures that receive signals from other neurons and transmit them to the cell body.
- Axons: long fibers that carry signals away from the cell body to other neurons or muscles.
Neurons communicate with each other at synapses, which are specialized junctions where the axon of one neuron meets the dendrite of another neuron. At the synapse, chemical signals called neurotransmitters are released, which transmit signals from one neuron to the next.
Summary: How the Nervous System Works
The nervous system works by transmitting signals from one neuron to another, and ultimately to the brain. The signals are transmitted via a long extension called the axon, which can be up to a meter long. The signals are received by dendrites, which act like antennae and pass the signals on to the cell body.
Conclusion
In summary, the nervous system is a complex and vital system that is responsible for the communication between different parts of the body. It receives information from our senses, processes it, and sends out appropriate responses. The nervous system controls our voluntary and involuntary movements, and it is made up of specialized cells called neurons. Understanding how the nervous system works is essential for maintaining good health.