The endocrine system is an essential part of our body that influences almost every physiological function. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the body's balance and overall health. In this article, we will explore how the endocrine system works and dive deep into its significance, functions, and common disorders. Keep reading to learn more! 📚
IN THIS ARTICLEWhat is the Endocrine System?
The endocrine system comprises various glands that secrete hormones, which are chemical messengers responsible for coordinating various bodily functions. These hormones regulate metabolism, growth, development, emotions, mood, sexual function, and even sleep patterns. The glands in the endocrine system are found throughout the body and differ in size and function.
Anatomy of the Endocrine System
The endocrine system consists of several glands, including:
- Hypothalamus: Located in the brain, the hypothalamus controls the endocrine system using information from the nervous system. It regulates mood, hunger and thirst, sleep patterns, and sexual function.
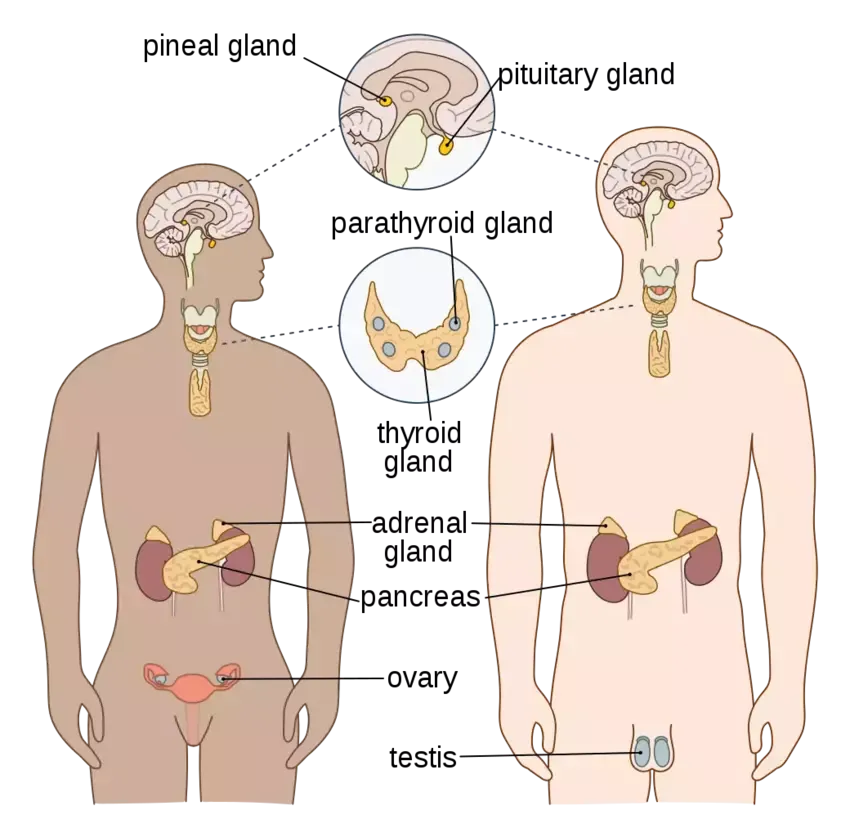
- Pituitary: A pea-sized gland at the base of the brain, the pituitary controls several other glands, including the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, ovaries, and testicles.
- Thyroid: A butterfly-shaped gland in the front of the neck, the thyroid is responsible for metabolism.
- Parathyroid: These four tiny glands control the level of calcium in the body, essential for the heart, kidneys, bones, and nervous system.
- Adrenal: Located on top of each kidney, these glands control metabolism, blood pressure, sexual development, and stress response.
- Pineal: This gland manages the sleep cycle by releasing melatonin, a hormone that induces sleepiness.
- Pancreas: A part of both the endocrine and digestive systems, the pancreas produces insulin, which controls blood sugar levels.
- Ovaries: In women, the ovaries release sex hormones like estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone.
- Testes: In men, the testes produce sperm and release the hormone testosterone, which affects sperm production, muscle strength, and sex drive.
Functions of the Endocrine System
The endocrine system continuously monitors the hormone levels in the blood. When the hormone levels reach a certain point, the pituitary gland signals other glands to stop producing and releasing hormones. If the hormone levels dip below a certain point, the pituitary gland can instruct other glands to produce and release more. This process is called homeostasis.
Hormones affect a wide range of processes in the body, including:
- Metabolism
- Growth and development
- Emotions and mood
- Fertility and sexual function
- Sleep
- Blood pressure
Many factors, such as illness, stress, and certain medications, can cause a hormone imbalance, leading to various health problems.
How Does the Endocrine System Work? 🧪
The endocrine system is a complex network of glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream. These hormones act as chemical messengers, traveling through the circulatory system to reach target cells and organs. By binding to specific receptors on the target cells, hormones trigger various physiological responses that help regulate essential functions such as growth, metabolism, and reproduction. Here's a closer look at the endocrine system's functioning:
Hormone Production and Release 🌱
Each gland within the endocrine system is responsible for producing and releasing specific hormones. The hypothalamus, a region in the brain, acts as the primary control center for the endocrine system. It receives input from various parts of the body, processes the information, and responds by stimulating or inhibiting the release of hormones from the pituitary gland.
The pituitary gland, also known as the "master gland," is responsible for producing and releasing various hormones that regulate other glands within the endocrine system. For instance, the pituitary gland releases thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) to stimulate the thyroid gland, which in turn produces hormones that regulate metabolism.
Hormone Regulation and Feedback Loops 🔄
The endocrine system uses feedback loops to maintain optimal hormone levels in the body. Feedback loops involve a series of reactions that help regulate hormone production and secretion.
Negative feedback loops are the most common form of hormone regulation. In these loops, the presence of a hormone inhibits its further production and release. For example, when the thyroid gland releases thyroid hormones, these hormones act on the pituitary gland to suppress TSH production. This inhibition prevents the overproduction of thyroid hormones.
Positive feedback loops, on the other hand, are less common but still crucial. In these loops, the presence of a hormone stimulates further production and release. For example, during childbirth, the hormone oxytocin stimulates uterine contractions, which in turn cause the release of more oxytocin, leading to stronger contractions.
Target Cells and Hormone Action 🎯
Hormones affect only specific target cells that have the appropriate receptors for that particular hormone. When a hormone reaches its target cell, it binds to the receptor, triggering a series of reactions within the cell that lead to a particular response. Hormones can act by altering the target cell's gene expression, activating or deactivating enzymes, or modifying the cell's membrane potential.
Through this intricate process, the endocrine system maintains the body's internal balance and ensures that the body's various functions work in harmony. Understanding the endocrine system's working mechanism helps us appreciate the vital role it plays in our overall health and well-being.
Common Conditions and Disorders of the Endocrine System
Several conditions and disorders can affect the endocrine system, leading to various health problems. Some common disorders include:
- Diabetes: Affects how the body uses energy from food, caused by insufficient insulin production or insulin resistance.
- Thyroid disorders: Hypothyroidism (low hormone production) and hyperthyroidism (excessive hormone production) affect thyroid gland function.
- Hypogonadism: In men, low testosterone levels can cause erectile dysfunction, memory and concentration problems, changes in muscle strength, and low sex drive.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): Hormonal imbalance in women, causing irregular periods, abnormal hair growth, excess acne, weight gain, and potentially leading to diabetes, an increased risk of metabolic syndrome, and infertility.
- Osteoporosis: A condition where bones become brittle and weak, caused by low estrogen levels in women and low testosterone levels in men. It can also be caused by an overactive parathyroid gland (hyperparathyroidism).
Endocrine disruptors, chemicals found in pesticides, plastics, cosmetics, and even food and water, can also affect the endocrine system. These disruptors can cause a wide range of problems throughout the body by altering how hormones send messages.
Prevalence of Endocrine Disorders 📊
- Diabetes: Almost 10% of people in the United States have diabetes, and 27% have prediabetes.
- Thyroid disorders: About 20 million Americans have thyroid disease, with women being five times more likely than men to develop the condition.
- Hypogonadism: Approximately 40% of men over 45 have low testosterone. Testosterone levels naturally drop with age, and other factors like diet, weight, and health problems can also affect levels.
- PCOS: Affecting 5% to 10% of adult women in the U.S., PCOS is a leading cause of infertility.
- Osteoporosis: Over half of adults over age 50 have osteoporosis, with the condition being more common in women than in men.
Maintaining a Healthy Endocrine System 🍏
To keep your endocrine system healthy, adopt a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise, a balanced diet, and routine healthcare provider visits. If you have a family history of diabetes, thyroid disorders, or PCOS, talk to your healthcare provider about managing these conditions to avoid hormone imbalances that can lead to health problems.
When to Call Your Doctor 📞
Contact your healthcare provider if you experience any of the following symptoms, as they could indicate a serious health condition such as diabetes:
- Frequent urination
- Extreme thirst, even after drinking plenty of water
- Persistent nausea or stomach pain
- Sudden weight loss or unexplained weight gain
- Severe exhaustion or weakness
- Excessive sweating
- Sudden episodes of rapid heartbeats or elevated blood pressure
- Developmental or growth delays
By understanding the vital role the endocrine system plays in our body and taking steps to maintain its health, we can ensure optimal well-being and reduce the risk of various health problems. Stay informed and proactive to maintain a balanced and healthy life! 🌟
References
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK). Endocrine System. Available at: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/endocrine-diseases. Accessed 5/3/2023.
- Hormone Health Network. What is the Endocrine System? Available at: https://www.hormone.org/what-is-endocrinology/the-endocrine-system. Accessed 5/3/2023.
- American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS). How Does the Endocrine System Work? Available at: https://www.science.org/content/article/how-does-endocrine-system-work. Accessed 5/3/2023.
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Hormones and the Endocrine System. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279388/. Accessed 5/3/2023.
- Harvard Medical School. The Endocrine System. Available at: https://hms.harvard.edu/sites/default/files/assets/Sites/Longwood_Seminars/Longwood%20Seminars%20-%20The%20Endocrine%20System.pdf. Accessed 5/3/2023.